A ratio under 1.00 indicates that the company’s debts due in a year or less are greater than its cash or other short-term assets expected to be converted to cash within a year or less. Traditionally, calculating the quick ratio was a manual process, where finance teams would pull data from various sources, including balance sheets and accounts, to gather current assets and liabilities. First, the quick ratio excludes inventory and prepaid expenses from liquid assets, with the rationale being that inventory and prepaid expenses are not that liquid. Prepaid expenses can’t be accessed immediately to cover debts, and inventory takes time to sell. Outside of a company, investors and lenders may consider a company’s current ratio when deciding if they want to work with the company.

Investment Decisions – Why Is the Current Ratio Important to Investors and Stakeholders?
This article and related content is not a substitute for the guidance of a lawyer (and especially for questions related to GDPR), tax, or compliance professional. When in doubt, please consult your lawyer tax, or compliance professional for counsel. Sage makes no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness or accuracy of this article and related content. Learn how automation is revolutionising the finance sector, streamlining operations and improving work-life balance. Regular monitoring gives you time to adjust spending, defer expenses, or focus on collections as needed. Current liabilities are obligations that are to be settled within 1 year or the normal operating cycle.
Inventory consideration:
The current ratio is part of what you need to understand when investing in individual stocks, but those investing in mutual funds or exchange-trade funds needn’t worry about it. The offers that appear on this site are from companies that compensate us. But this compensation does not influence the information we publish, or the reviews that you see on this site.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
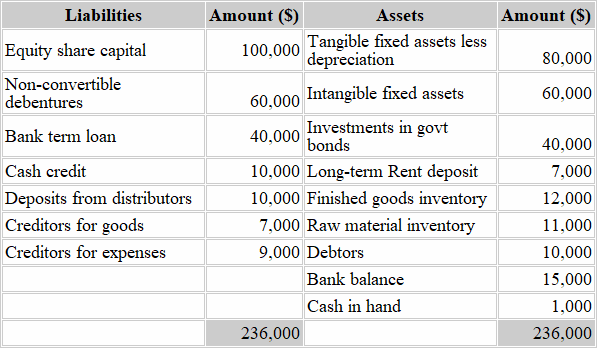
A high current ratio indicates that a company has a solid ability to meet its short-term obligations. In contrast, a low current ratio may suggest a company faces financial difficulties. The current ratio evaluates a company’s ability to pay its short-term liabilities with its current assets. The quick ratio measures a company’s liquidity based only on assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days or less. The current ratio (also known as the current asset ratio, the current liquidity ratio, or the working capital ratio) is a financial analysis tool used to determine the short-term liquidity of a business. It takes all of your company’s current assets, compares them to your short-term liabilities, and tells you whether you have enough of the former to pay for the latter.
Understanding the Current Ratio
Learn the skills you need for a career in finance with Forage’s free accounting virtual experience programs. This can be achieved through better forecasting and demand planning, more efficient production processes, or just-in-time inventory management. To give you an idea of sector ratios, we have picked up the US automobile sector. This includes all the goods and materials a business has stored for future use, like raw materials, unfinished parts, and unsold stock on shelves. This account is used to keep track of any money customers owe for products or services already delivered and invoiced for.
- Traditionally, calculating the quick ratio was a manual process, where finance teams would pull data from various sources, including balance sheets and accounts, to gather current assets and liabilities.
- In this example, Company A has much more inventory than Company B, which will be harder to turn into cash in the short-term.
- For example, the inventory listed on a balance sheet shows how much the company initially paid for that inventory.
- For example, a normal cycle for the company’s collections and payment processes may lead to a high current ratio as payments are received, but a low current ratio as those collections ebb.
Public companies don’t report their current ratio, though all the information needed to calculate the ratio is contained in the company’s financial statements. Set a quick ratio benchmark that aligns with industry standards to ensure your business is well-positioned for stability and growth. We hope this guide has helped demystify the current ratio and its importance and provided useful insights for your financial analysis and decision-making. This is because inventory can be more challenging to convert into cash quickly than other current assets and may be subject to write-downs or obsolescence. Inventory management issues can also lead to a decrease in the current ratio. If the company holds too much inventory that is not selling, it can tie up cash and reduce the current ratio.
The current ratio equation is a crucial financial metric, that assesses a company’s short-term liquidity by comparing its current assets to its current liabilities. A ratio above 1 indicates the company can meet its short-term obligations, while below 1 suggests potential liquidity issues. It aids in evaluating a firm’s financial health and ability to cover immediate debts.
Larger companies may have a lower current ratio due to economies of scale and their ability to negotiate better payment terms with suppliers. Creditors and lenders often use the current ratio to assess a company’s creditworthiness. A high current ratio can make it easier for a company to obtain credit, while a low current ratio may make it more difficult to secure financing.
A company with a current ratio of less than 1 has insufficient capital to meet its short-term debts because it has a larger proportion of liabilities relative to the value of its current assets. A company with a current ratio of less than intro to forensic and investigative accounting chp 1 flashcards one doesn’t have enough current assets to cover its current financial obligations. The current ratio is a liquidity and efficiency ratio that measures a firm’s ability to pay off its short-term liabilities with its current assets.

